Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMJSBT6)
| Drug Name |
SILODOSIN
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Silodosin; 160970-54-7; Rapaflo; Urief; Silodyx; Urorec; KMD-3213; Silodosin-d6; UNII-CUZ39LUY82; KMD 3213; KAD 3213; CUZ39LUY82; CHEMBL24778; KAD-3213; (R)-1-(3-hydroxypropyl)-5-(2-((2-(2-(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)phenoxy)ethyl)amino)propyl)indoline-7-carboxamide; 1-(3-hydroxypropyl)-5-[(2R)-2-[2-[2-(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)phenoxy]ethylamino]propyl]-2,3-dihydroindole-7-carboxamide; 160970-64-9; Q-102517; Rapflo
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Humans and other mammals
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
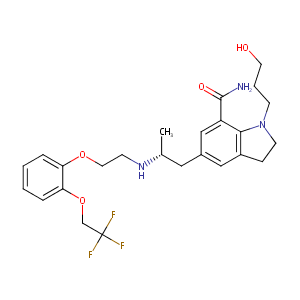 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 1 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 495.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 3.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 13 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug Transporter (DTP) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Expression Atlas of This Drug
| The Studied Disease | Benign prostatic hyperplasia | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICD Disease Classification | GA90 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Expression Atlas (MEA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from SILODOSIN (Comorbidity)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug Inactive Ingredient(s) (DIG) and Formulation(s) of This Drug
References
| 1 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 493). | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | FDA Approved Drug Products: RAPAFLO (silodosin) Capsule for oral use | ||||
| 3 | Estimating the safe starting dose in phase I clinical trials and no observed effect level based on QSAR modeling of the human maximum recommended daily dose | ||||
| 4 | Trend Analysis of a Database of Intravenous Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Humans for 1352 Drug Compounds | ||||
| 5 | Pharmacophore identification of alpha(1A)-adrenoceptor antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2005 Feb 1;15(3):657-64. | ||||
| 6 | Pharmacokinetics and disposition of silodosin (KMD-3213)]. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2006 Mar;126 Spec no.:237-45. | ||||
| 7 | The influence of UGT2B7, UGT1A8, MDR1, ALDH, ADH, CYP3A4 and CYP3A5 genetic polymorphisms on the pharmacokinetics of silodosin in healthy Chinese volunteers. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2013;28(3):239-43. | ||||
| 8 | Silodosin for benign prostatic hyperplasia. Ann Pharmacother. 2010 Feb;44(2):302-10. | ||||
| 9 | Pharmacokinetics and disposition of silodosin (KMD-3213). Yakugaku Zasshi. 2006 Mar;126 Spec no.:237-45. | ||||
| 10 | Carvedilol selectively inhibits oscillatory intracellular calcium changes evoked by human alpha1D- and alpha1B-adrenergic receptors. Cardiovasc Res. 2004 Sep 1;63(4):662-72. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2004.05.014. | ||||
| 11 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "Australian Product Information.". | ||||
| 12 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "UK Summary of Product Characteristics.". | ||||
| 13 | Product Information. Balversa (erdafitinib). Janssen Products, LP, Horsham, PA. | ||||
| 14 | Product Information. Rapaflo (silodosin). Watson Pharmaceuticals, Corona, CA. | ||||
| 15 | Aronowitz JS, Chakos MH, Safferman AZ, Lieberman JA "Syncope associated with the combination of clozapine and enalapril." J Clin Psychopharmacol 14 (1994): 429-30. [PMID: 7884028] | ||||
| 16 | Chrysant SG "Experience with terazosin administered in combination with other antihypertensive agents." Am J Med 80 (1986): 55-61. [PMID: 2872808] | ||||
| 17 | Product Information. Harvoni (ledipasvir-sofosbuvir). Gilead Sciences, Foster City, CA. | ||||
| 18 | Product Information. Juxtapid (lomitapide). Aegerion Pharmaceuticals Inc, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 19 | Product Information. Tabrecta (capmatinib). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 20 | Product Information. Reyvow (lasmiditan). Lilly, Eli and Company, Indianapolis, IN. | ||||
| 21 | Ban TA "Drug interactions with psychoactive drugs." Dis Nerv Syst 36 (1975): 164-6. [PMID: 1116424] | ||||
| 22 | Product Information. Varubi (rolapitant). Tesaro Inc., Waltham, MA. | ||||
| 23 | Product Information. Xeglyze (abametapir topical). Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Inc, Upper Saddle River, NJ. | ||||
| 24 | Product Information. Xenleta (lefamulin). Nabriva Therapeutics US, Inc., King of Prussia, PA. | ||||
| 25 | Product Information. Tavalisse (fostamatinib). Rigel Pharmaceuticals, South San Francisco, CA. | ||||
